Gegenwärtig hat das Aufkommen der dritten Halbleitergeneration, vertreten durch SiC und GaN, dazu geführt, dass sich Leistungsmodule in Richtung Miniaturisierung, Hochspannung, Hochstrom und hohe Leistungsdichte entwickeln, was bei der Verwendung zu höherer Wärmeentwicklung führt und hohe Anforderungen an die Wärmeableitungspakete der Geräte stellt. Bei der neuen Generation von Hochleistungsmodulen übernimmt das Keramiksubstrat hauptsächlich die Rolle des Chipträgers, der elektrischen Isolierung und des Wärmeleitkanals, und Siliziumnitridkeramik ist aufgrund seiner Vorteile der hohen Wärmeleitfähigkeit und der hohen mechanischen Eigenschaften zu einem Wärmeableitungssubstratmaterial mit großem Anwendungspotenzial geworden.
Die Frage, wie man ein hochleistungsfähiges Siliziumnitridsubstrat mit sowohl mechanischen Eigenschaften als auch Wärmeleitfähigkeit erhält, ist heute eines der wichtigsten Themen der Branche. Aufgrund des niedrigen Diffusionskoeffizienten von Si- und N-Atomen im Siliziumnitridkeramiksubstrat müssen Phasenumwandlung, Kornentwicklung und Verdichtung durch Flüssigphasensintern erreicht werden. Daher ist es eine effektive Methode, die mechanischen und thermischen Eigenschaften von Siliziumnitridkeramiken zu verbessern, die Flüssigphase und Mikromorphologie im Sinterprozess mit geeigneten Sinteradditiven anzupassen.
Arten von nichtoxidischen Sinterhilfsmitteln
Fluorid
In Silikatlösungen können Fluoratome die Struktur des Silikatnetzwerks zerstören und es zersetzen, was die Temperatur und Viskosität der Flüssigphasenbildung senkt und die Sinterverdichtung fördert. Beispielsweise kann die Verwendung von MgF2 anstelle von MgO als Sintermittel eine Flüssigphase bei niedrigerer Temperatur bilden, die Verdichtung von Keramik beschleunigen und die Korngröße mit zunehmender MgF2-Zugabe erhöhen, was die Wärmeleitfähigkeit von Siliziumnitridkeramik effektiv verbessern kann. Darüber hinaus gibt es LiF, Seltenerdfluorid, binäres Fluorid usw.
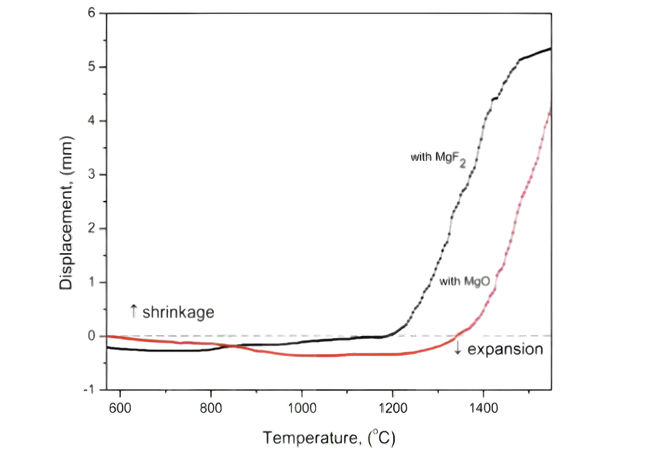
Die Verschiebungstemperaturkurve von Si3N4-Keramiken wurde unter Verwendung von MgF2 und MgO als Sinteradditive erstellt.
Fluorid-Sinteradditive verhindern die Einführung zusätzlicher Sauerstoffatome in das System, verringern die Aktivität von SiO2 in der Flüssigphase und verhindern die Bildung von Gittersauerstoff während des Lösungsfällungsprozesses. Gleichzeitig verringert die atomare Energie des Fluors die Viskosität der Flüssigphase, hilft bei der Bildung der Flüssigphase bei niedriger Temperatur, fördert die Entwicklung großer β-Si3N4-Körner und die hergestellten Siliziumnitridkeramiken weisen einen niedrigen Gittersauerstoffgehalt und einen niedrigen interkristallinen Phasengehalt mit Wärmeleitfähigkeit sowie eine hohe Wärmeleitfähigkeit der Keramik auf. Eine übermäßige Verflüchtigung von SiF4 erhöht jedoch die Porosität der Keramik und verringert die mechanischen Eigenschaften und die Wärmeleitfähigkeit, sodass die entsprechende Zugabemenge kontrolliert werden muss.
Nitride und stickstoffhaltige Verbindungen
Metal nitride has good compatibility with silicon nitride ceramics, and is often used as a sintering assistant to prepare silicon nitride ceramic materials, which can enhance the thermal conductivity of silicon nitride ceramics and strengthen its mechanical properties. MgSiN2, as a potential high thermal conductivity ceramic, has attracted much attention as a sintering aid for silicon nitride ceramics in recent years. At high temperature, SiO2 on the surface of MgSiN2 and Si3N4 powder will form Mg-Si-O-N liquid phase and promote densification. In addition, a portion of Si and N atoms are separated out in the form of Si3N4 to optimize grain boundaries. In recent years, by using MgSiN2 instead of MgO, researchers have prepared silicon nitride ceramics with high thermal conductivity and excellent mechanical properties at lower sintering temperature and shorter holding time. Li Jiangtao's team from the Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences prepared MgSiN2 in batches through self-propagating sintering, laying a material foundation for the large-scale application of MgSiN2. It is expected to be used as an efficient sintering aid for silicon nitride ceramics with high thermal conductivity.
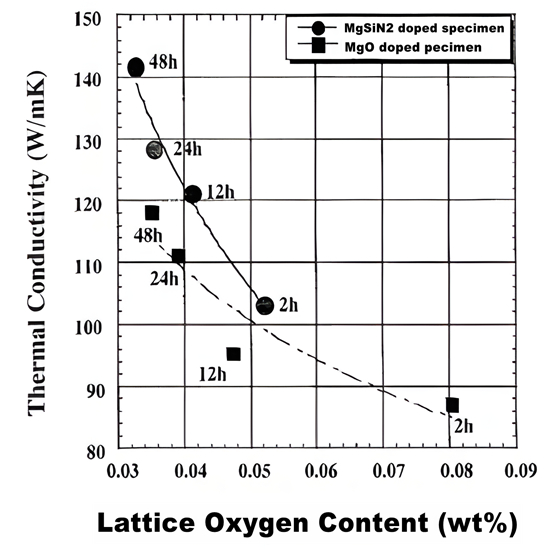
The silicon nitride ceramics with low lattice oxygen content and high thermal conductivity were prepared by using MgSiN2 as sintering assistant
In addition, some researchers used solid phase reaction to synthesize a new non-oxide sintering agent Y2Si4N6C to replace Y2O3 as a sintering agent, which not only has low lattice oxygen content, but also weakened the scattering of phonons by intergranular phase and grain boundary film, which can greatly improve the thermal conductivity of silicon nitride ceramic substrate. However, the preparation process of Y2Si4N6C is complex, and it cannot be synthesized in large quantities for the time being, which limits its application.
Borides
The densified Si3N4 ceramics with LaB6 as the sintering agent do not introduce additional oxygen into the system, and can remove lattice oxygen through the dissolution precipitation process, improve the thermal conductivity of β-Si3N4 grains, and at the same time, the content of low thermal conductivity intercrystalline phases is less, the grain size is larger, and the phonon scattering between grains is weakened. This is because during the sintering process, B atoms enter the glass network, and the formed [BO3]- structural unit will replace the [SiO4]- structural unit in the original network, destroying the integrity of the glass network, reducing the liquid phase viscosity, and thus promoting low temperature sintering.
Silicides
It has been found that iron silicide (FeSix) has a certain regulatory effect on the phase transition and grain growth of silicon nitride ceramics. For example, FeSi2 can generate β-Si3N4 phase before the α-Si3N4 phase transition, providing nucleation and growth points for the later α-Si3N4 phase transition. It is helpful to regulate the phase transition and grain growth process in the sintering of silicon nitride ceramics. ZrSi2 can react with SiO2 on the surface of silicon nitride powder to produce ZrO2 and β-Si3N4 crystal seeds. In situ ZrO2 and MgO assistant form a low temperature eutectic liquid phase, which promotes ceramic densification and β-Si3N4 grain development through dissolution precipitation mechanism. Due to the consumption of SiO2 by ZrSi2, the oxygen content in the liquid phase is reduced, thereby impeding the generation of lattice oxygen dynamically and reducing lattice defects. In addition, Zr elements in the sintered body are precipitated in the form of ZrN (or ZrO2) phase, and there is no obvious amorphous grain boundary film between Si3N4 grains, which reduces the scattering of phonons at the grain boundaries. Thanks to the above three factors, the thermal conductivity of Si3N4 has been greatly improved. However, the difficulty of both thermal conductivity and mechanical properties limits the application of ZrSi2 as a sintering aid for high-conductivity silicon nitride ceramics.
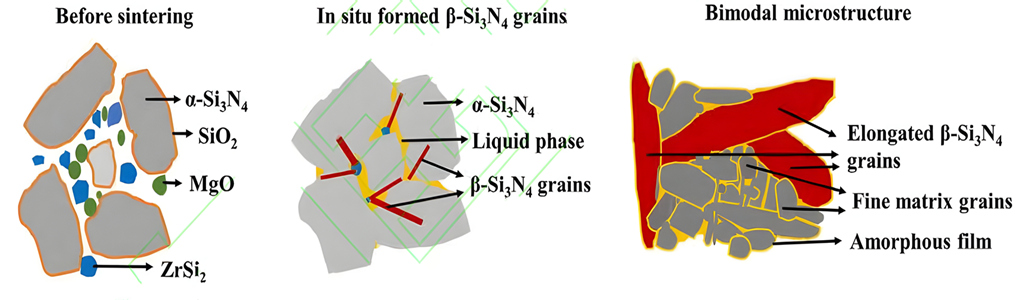
Schematic diagram of densification mechanism of silicon nitride ceramics containing ZrSi2-MgO additive
Hydrides and Metal Particles
Metal hydride is a commonly used oxygen consumption agent in powder metallurgy industry, which is decomposed into metal elements and H2 at high temperatures, H2 can remove the oxide layer on the surface of metal particles, and the highly active metal elements generated by decomposition play the role of absorbing impurity oxygen in the metal matrix, which can effectively improve the performance of metal products. Rare earth hydrides such as YH2 can reduce the activity of SiO2 in the liquid phase and facilitate the removal of lattice oxygen during dissolution precipitation. In addition, the "nitrogen-rich" liquid phase formed by the addition of YH2 is also conducive to the nucleation and development of β-Si3N4, and the grain size is significantly larger than that of Y2O3 additive system. However, excessive hydride makes the liquid viscosity too high, inhibits the densification process, and the fully developed β-Si3N4 grains cross to form a porous skeleton, which can not prepare high density silicon nitride ceramics. Therefore, it is still necessary to determine the optimal amount of rare earth hydride according to the oxygen content of α-Si3N4 raw material powder.
Ternary Layered Compound
The fracture toughness can be improved by introducing layered compounds into silicon nitride ceramic matrix through crack deflection, bridge and other mechanisms. In recent years, researchers have investigated the effect of layered compounds on the thermal conductivity of silicon nitride ceramics, and found that layered compounds can effectively improve the mechanical thermal properties of ceramics. YB2C2 can react with SiO2 on the surface of silicon nitride powder to reduce the liquid phase oxygen content and promote densification. The remaining YB2C2 layer improves the bending strength and fracture toughness of the ceramics through crack deflection mechanism.
Carbon, Silicon Sintering Additives
Carbon is widely used to remove oxygen impurities from ores because of its strong reducibility. In the study of silicon nitride, a small amount of carbon can promote α→β phase transition in silicon nitride sintering. Carbon thermal reduction deoxygenation can adjust the composition and properties of the liquid phase, and then regulate the relative rate of phase transition and densification, so that the silicon nitride ceramics with good morphology can be obtained without adding β-Si3N4 seed.
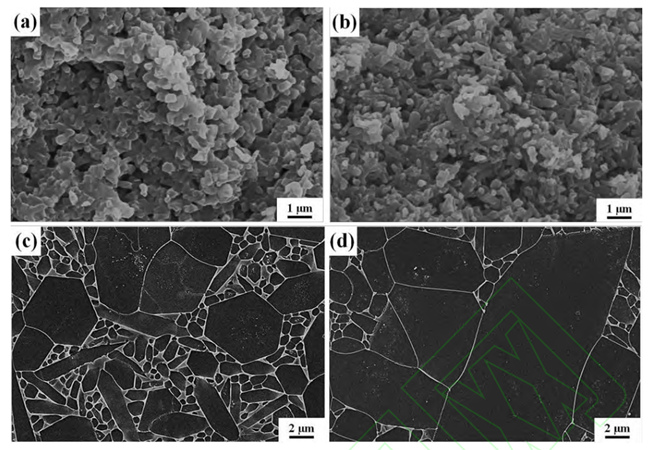
(a, c) Sample microstructure after nitriding without addition and (b, d) sample microstructure
after nitriding with buried powder containing C (a, b) and microstructure of silicon nitride after air
It is worth noting that the introduction of C needs to be controlled precisely in the sintering system of silicon nitride ceramics, the addition amount is too small, and the control effect of liquid phase is not good. Excessive addition will lead to residual SiC in the sample, which will adversely affect the density and electrical properties of silicon nitride ceramics. The results show that Si can also remove the surface oxide layer by silicothermal reduction reaction with SiO2. Unlike toner, which requires precise control of the amount of addition, excess Si is nitrided to Si3N4 in a nitrogen atmosphere, without the formation of harmful by-products.
The research of optimizing raw material powder of silicon nitride by carbothermal reduction and silicothermal reduction, and improving the performance of silicon nitride ceramics by means of liquid phase regulation provides a solution for the preparation of high thermal conductivity silicon nitride ceramics by using low-cost silicon nitride powders with high oxygen content.
Vor dem Hintergrund, dass Siliziumnitridpulver mit niedrigem Gittersauerstoffgehalt noch keinen Durchbruch erzielt haben, ist es eine wirtschaftliche und effektive Möglichkeit, die Wärmeleitfähigkeit von Siliziumnitridkeramiken zu verbessern, indem man Nichtoxide anstelle entsprechender Oxidsinterzusätze verwendet und die Zusammensetzung der flüssigen Phase anpasst. Mit der kontinuierlichen Optimierung des Siliziumnitrid-Rohmaterialpulvers, der kontinuierlichen Entwicklung neuer multifunktionaler Sinterzusätze und der kontinuierlichen Verbesserung der Form- und Sinterprozesse ist die großtechnische Produktion von hochfesten und hochwärmebeständigen Si3N4-Substraten Realität geworden, was eine starke Unterstützung für die Entwicklung von Leistungshalbleiterbauelementen sein wird.





























